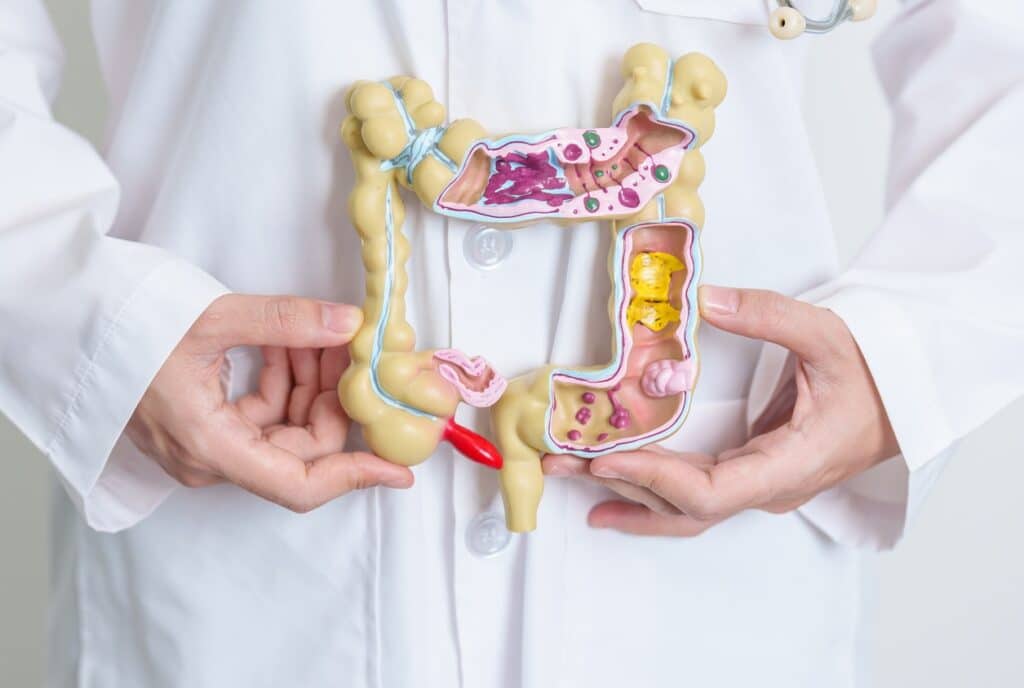
Ulcerative colitis causes inflammation of the large intestine, also known as the colon. Doctors categorize ulcerative colitis as a type of inflammatory bowel disease. In ulcerative colitis, the lining of the large intestine becomes inflamed and develops open sores, known as ulcers. These ulcers produce mucus and pus, which causes abdominal pain and feeling like you need to empty your bowels frequently.
Ulcerative colitis symptoms can vary, depending on the severity of inflammation and where it occurs. Depending on which part of the colon is affected, symptoms may include:
The exact cause of ulcerative colitis is unknown. Previously, diet and stress were suspected, but now doctors know these may aggravate, but don't cause colitis. When your body tries to fight off a virus or bacterium, an abnormal response causes the immune system to attack cells in the digestive tract. Some risk factors may include age (colitis often begins before age 30) and family history.
Your doctor will make a diagnosis based on your medical history, a physical examination, and various tests. Following this, your provider will typically evaluate your colon, using a sigmoidoscopy or colonoscopy.
The exact cause of ulcerative colitis is unknown, but several factors may contribute to its development. While no specific risk factors guarantee someone will develop the condition, certain factors are associated with an increased risk of ulcerative colitis:
It's important to note that while these factors are associated with an increased risk, many people with ulcerative colitis do not have any identifiable risk factors. Additionally, the interplay between genetics, environment, and the immune system in the development of the disease is complex and not fully understood. If someone has concerns about their risk of ulcerative colitis, they should consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice based on their medical history and family background.
Chronic bleeding from ulcerative colitis can cause a shortage of red blood cells, a condition known as anemia. Because ulcerative colitis interferes with nutrient absorption, some people with the condition may experience weight loss or problems with their skin, eyes, joints, liver, or kidneys.
Peptic ulcers will get worse if not treated. Treatment may include medicines to reduce stomach acids or antibiotics to kill H. pylori. Antacids and milk can't heal peptic ulcers. Avoiding alcohol and not smoking can help. You may need surgery if your ulcers don't heal.
About a million people in the US have ulcerative colitis.
Ulcerative colitis usually develops between the ages of 15 and 30, although it can appear at any age. Inflammation associated with ulcerative colitis can flare several times through life to cause recurring signs and symptoms.